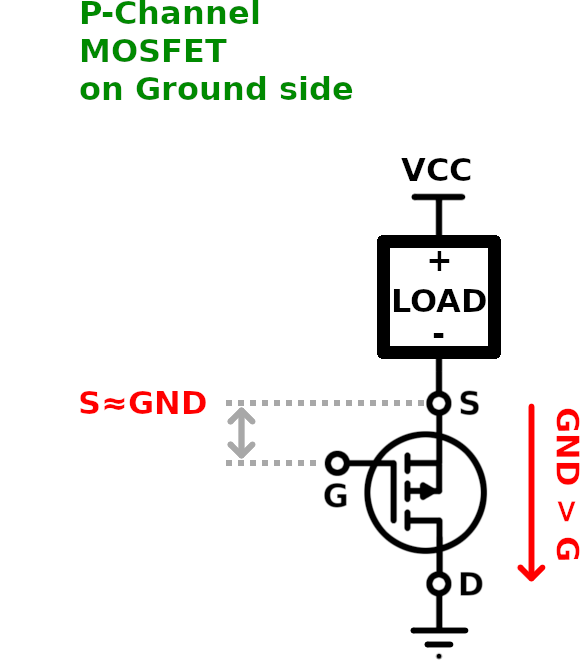
- Mosfet P Channel Circuit
- Logic Level Mosfet P-channel
- Mosfet P Channel Smd
- Mosfet P Channel Switch
- Mosfet P Channel Switch
- Mosfet P Channel Switch Normally Closed
Discrete Semiconductor Products - Transistors - FETs, MOSFETs - Single are in stock at Digikey. Discrete Semiconductor Products ship same day. P-channel, MOSFETs manufactured by Vishay, a global leader for semiconductors and passive electronic components.

Webmaster Homepage and contact information.
Hobby Electronics Homepage.
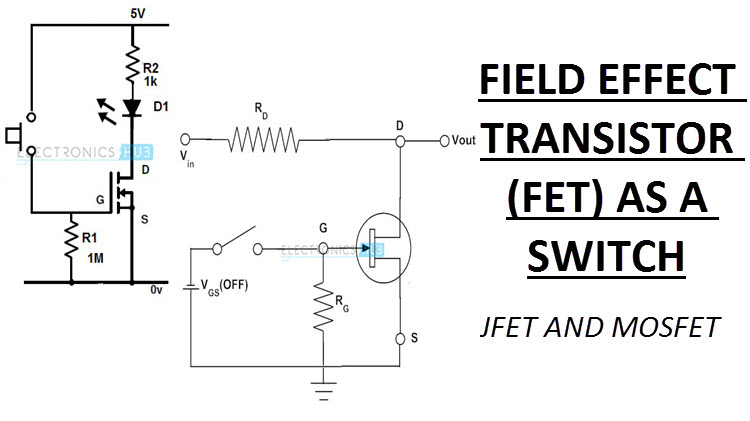
This tutorial will explore the use of a P-channel and N-channel MOSFETs as a power switch and general transistor theory. This switch will operate on the positive side of a power supply with a negative common. This is for use with 5-volt micro controllers such as Arduino.
Pictured above is the basic electrical connections for Arduino and most modern micro-controllers. We have a negative common and a 5-volt Vcc. That dictates how we connect any driver transistor to the I/O pins. In addition each Arduino I/O pin can source/sink an absolute maximum of 40mA. (Note: operate at 20mA.)
First note that all MOSFETs are voltage operated devices and don't rely on a base current like a bipolar transistor. In many cases gate drive voltages below 5-volts won't work without a bipolar transistor switching in a higher voltage.
Update Dec. 2019. Many micro-controllers today are using 3.3-volt Vcc. This is also true of Raspberry Pi. I found two MOSFETs that work at 3.3-volts.
The IRFZ44N is an N-channel device rated at 55V and RDS(on) resistance of 0.032 Ohms max. The other is a P-channel device rated at 55V and a RDS(on) of 0.02 Ohms max.
See the following spec sheets:
Referring to Plate 1 whenever the voltage difference between the gate (G) and source (S) exceeds around 5-volts this opens a conductive channel between source (S) and drain (D) allowing current flow from the source back to the power supply. (Here we are using electron flow from negative to positive.)
This is often known as a series pass configuration.
Looking again at Plate 1 with no input to the base of Q1 the collector voltage rises to Vcc and with no difference in potential across Rgs Q6 and Q8 are turned off.
Mosfet P Channel Circuit
Applying 5-volts to the base resistors of Q8 and Q6 (plate 1) forward biases their base-emitter junctions allowing a small current flow Ib. Depending on the DC gain (hfe) of the individual transistors the base current is multiplied to produce Ic. The relationship is as follows:
Ie = Ib + Ic; Ib * hfe = Ic.
The base current Ib is determined by Vin - 0.6 / Rb. The 0.6 volts is the voltage drop across the BE junction. Let's say Q1 and Q7 are 2N2222As that have minimum hfe of 90 and we desire an Ic of 20 mA. Here is how this will work:
Now some issues on switching transistors. We want them operating in their saturation mode where any additional base current will produce no increase in collector current (Ic). When making these calculations a transistor spec sheet gives a range for hfe, assume the lowest value. Next as long as we don't exceed the max base current rating assume extra current. In this case I would use a 2.2K for Rb.
When a bipolar transistor is operating at saturation the emitter-collector voltage equals 0.5V. In the case of MOSFETs Q6 and Q8 we want those operating in saturation mode as well. With a 12-volt difference between gate-source this assures a fast, hard turn on. At saturation MOSFETS such as the IRF630 and IRF9630 have a drain-source resistance of 0.4 and 0.8 ohms respectively.
So Let's find Rgs where we want to drop 11.5 volts:
Let's assume a much higher value of say 10K to assure the desired voltage drop. Again we have lots of room to play with to assure saturation of all four transistors. Note that in reality Rgs sets the current level when Q1 and Q7 are in saturation mode.
Logic Level Mosfet P-channel
MOSFET Gate-Source Breakdown
Mosfet P Channel Smd
One final issue is the gate-source breakdown voltage of both MOSFETs or Vgs. For the IRF630 and IRF9630 this is 20 volts. The 24-volts in Fig. A would damage Q8. The 10-volt Zener in series with Q7's collector will keep this within a safe margin.
Plate 4
Uses
There are number of advantages to the above circuits. A low source-drain turn on resistance means more power is delivered to the load and less heating of series pass MOSFETs. The ability to operate at 5-volts makes direct connections to a micro-controller a cinch. In addition this can be pulse-width-modulated to control motor speed on a say H-bridge circuit.
The largest use of these circuits is H-bridge motor controls. They are used in conjunction with N-channel MOSFET switches.
Note that Rg (or Rgs) is used to bleed the charges off the MOSFET gates or else they may not turn off.
Have fun.
I hope the series was helpful. Any corrections, suggestions etc. e-mail me at lewis@bvu.net.
- Related:
- Why Your MOSFET Transistors Get Hot YouTube
- Issues on Connecting MOSFETs in Parallel YouTube
- Simple Circuits for Testing MOSFET Transistors YouTube
- New Nov. 2014
- Using the ULN2003A Transistor Array with Arduino YouTube
- Using the TIP120 & TIP120 Darlington Transistors with Arduino YouTube
- Using Power MOSFETS with Arduino YouTube
- Using PNP Bipolar Transistors with Arduino, PIC YouTube
- Using NPN Biploar Transistors with Arduino, PIC YouTube
- How to build a Transistor H-Bridge for Arduino, PIC YouTube
- Build a Power MOSFET H-Bridge for Arduino, PIC YouTube
Mosfet P Channel Switch
MALVERN, Pa., April 07, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. (NYSE: VSH) today introduced the world’s best AEC-Q101 qualified p-channel -80 V TrenchFET® MOSFET. With the lowest on-resistance of any -80 V p-channel device, the new Vishay Siliconix SQJA81EP increases power density and efficiency in automotive applications. In the compact 5.13 mm by 6.15 mm PowerPAK® SO-8L single package with gullwing leads, the SQJA81EP offers on-resistance down to 17.3 mΩ maximum / 14.3 mΩ typical at 10 V.
The on-resistance of the Automotive Grade MOSFET released today is 28 % lower than the closest competing device in the DPAK package — while offering a 50 % smaller footprint — and 31 % lower than previous-generation solutions. These values translate into energy savings by minimizing power losses from conduction while allowing higher output for increased power density. Combined with the SQJA81EP’s superior gate charge down to 52 nC at 10 V — which reduces losses from gate driving — the result is best in class gate charge times on-resistance, a critical figure of merit (FOM) for MOSFETs used in power conversion applications.
With high temperature operation to +175 °C, the device provides the ruggedness and reliability required for automotive applications such as reverse polarity protection, battery management, high side load switching, and LED lighting. In addition, the SQJA81EP’s gullwing leads allow for increased automatic optical inspection (AOI) capabilities and provide mechanical stress relief for increased board-level reliability.
The device’s -80 V rating provides the safety margin required to support several popular input voltage rails, including 12 V, 24 V, and 48 V systems. The MOSFET’s increased power density saves PCB space in these systems by reducing the number of components needed in parallel. In addition, as a p-channel device, the SQJA81EP enables simpler gate drive designs that don’t require the charge pump needed by its n-channel counterparts. Lead (Pb)-free, halogen-free, and RoHS-compliant, the MOSFET is 100 % Rg and UIS tested.
Samples and production quantities of the SQJA81EP are available now, with lead times of 14 weeks.
Vishay manufactures one of the world’s largest portfolios of discrete semiconductors and passive electronic components that are essential to innovative designs in the automotive, industrial, computing, consumer, telecommunications, military, aerospace, and medical markets. Serving customers worldwide, Vishay is The DNA of tech.™ Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. is a Fortune 1,000 Company listed on the NYSE (VSH). More on Vishay at www.Vishay.com.
The DNA of tech™ is a trademark of Vishay Intertechnology. TrenchFET and PowerPAK are registered trademarks of Siliconix incorporated.
Mosfet P Channel Switch
Vishay on Facebook:http://www.facebook.com/VishayIntertechnology
Vishay Twitter feed:http://twitter.com/vishayindust
Share it on Twitter:http://twitter.com/intent/tweet?text=.@vishayindust introduces the new Vishay Siliconix SQJA81EP, the world's best AEC-Q101 qualified p-channel -80 V TrenchFET MOSFET. - https://bit.ly/3fUTnxo
Link to product datasheet:
http://www.vishay.com/ppg?77266 (SQJA81EP)
Link to product photo:
https://www.flickr.com/photos/vishay/albums/72157718827308616
Mosfet P Channel Switch Normally Closed
For more information please contact:
Vishay Intertechnology
Peter Henrici, +1 408 567-8400
peter.henrici@vishay.com
or
Redpines
Bob Decker, +1 415 409-0233
Email: bob.decker@redpinesgroup.com
