Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations, and explanatory text. See full documentation for Jupyter Notebooks https://jupyter.readthedocs.io/. The text of the quick referance sheets comes from the IPython%quickref magic command. To download an image below, right click on the link and select 'Save Link As'. Basic Help.svg Download Magic Help.svg Download For more details of magic usage see the Built-in magic commands page in IPython's documentation.
- Jupyter Notebook Commands
- Jupiter Notebook Magic Commands Cheat Sheet Free
- Jupyter Notebook Keyboard Commands
Anaconda® is a package manager, an environment manager, a Python distribution, and a collection of over 720 open source packages. Here we have a basic cheatsheet for conda command line tool… enjoy!
Environments
Create environment
The default environment, the environment used when you aren’t in one, is called root.

Alternative:
Create an environment from an environment file
Listing environments
Activate environment
or just activate on windows
To leave the environment on OSX/Linux
or just deactivate on windows
Removing environments
Install packages
specify which version of a package
List packages
Update conda and packages
Saving and loading environments (use env, not your_env_name)
Update package
- To update a package conda update package_name
- If you want to update all packages in an environment, which is often useful, use conda update –all
Uninstall package
- To uninstall, use conda remove package_name
Search packages
- Search packages: conda search beautifulsoup
Sharing environments
When sharing your code on GitHub, it’s good practice to make an environment file and include it in the repository. This will make it easier for people to install all the dependencies for your code. I also usually include a pip requirements.txt file using pip freeze for people not using conda.
Saving and loading environments
- Saving an environment to a YAML file
Loading an environment from a YAML file
This will create a new environment with the same name listed in environment.yaml.
Listing environments
Removing environments
One thing that’s helped me tremendously is having separate environments for Python 2 and Python 3. I used conda create -n py2 python=2 and conda create -n py3 python=3 to create two separate environments, py2 and py3. Now I have a general use environment for each Python version.
Jupyter Notebook Commands
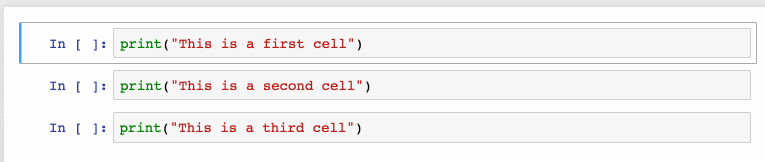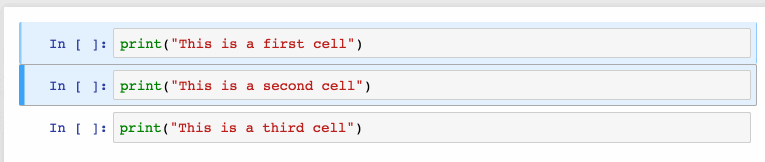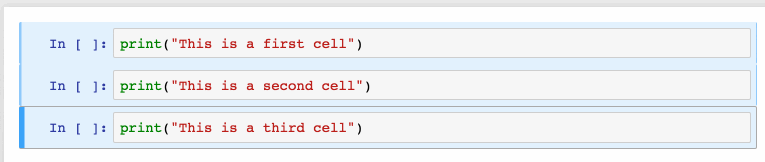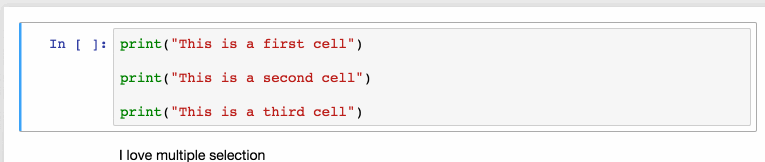
Install Jupyter notebooks
Jupyter notebooks are also available through pip with pip install jupyter notebook.
Launching the notebook server
Notebook Conda (nb_conda)
Allow us to create new environments, install packages, update packages, export environments and more. Additionally, with nb_conda installed you will be able to access any of your conda environments when choosing a kernel.
Tips and tricks working with Jupyter Notebooks
Magic keywords / commands
List of built-in magic commands here
Rendering matplotlib inline
time how long it takes for a whole cell to run:
Debugging in the Notebook
using %pdb. When you cause an error, you’ll be able to inspect the variables in the current namespace.To quit the debugger, simply enter q in the prompt
Jupiter Notebook Magic Commands Cheat Sheet Free
Converting Notebooks
to convert a notebook to an HTML file, in your terminal use
Are you starting to create machine learning models (using python programming) using JupyterLab or Jupyter Notebook? This post list down some commands which are found to be very useful while one (beginner data scientist) is getting started with using JupyterLabnotebook for building machine learning models.
Jupyter Notebook Keyboard Commands
- Notebook Operations: The following command helps to perform operations with the notebook.
- Ctrl + S: Save the notebook
- Ctrl + Q: Close the notebook
- Enter: While on any cell, you want to enter edit mode, press Enter.
- Cells Operation: The following commands help with performing operations on cells:
- J: Select the cell below the current cell; This command would be used to go through cells below the current cell; Once you reached to the desired cell, you could Shift + Enter to execute the command in the given cell.
- K: Select the cell above the current cell
- X: Cut the content of the current cell
- C: Copy the content of the current cell
- V: Paste the command copied into the below cell
- Shift + Enter: Run the selected cell and insert a cell below
- Ctrl + Enter: Run the selected cell but do not add the cell below; If this command is used, one could use B to enter a cell below.
- B: Enter a cell below. This command comes handy for entering the cell at any point. Very useful if you want to add a markdown note before/after execution of any command.
- D,D: Delete the cell
- Notes taking operations using Markdown editor: If you are a blogger, you would love these shortcuts. Very useful for taking notes while you are working on your models.
- M: Go to Markdown mode to write some notes in markdown format
- Y: Go to Code mode to continue working with code
Summary

In this post, you learned about some of the quick commands (Cheat sheet) which you could use for your reference while working with JupyterLab or Jupyter Notebook. Please feel free to suggest other commands that you found to be useful which are not listed above.
- First Principles Understanding based on Physics - April 13, 2021
- Precision & Recall Explained using Covid-19 Example - April 11, 2021
- Moving Average Method for Time-series forecasting - April 4, 2021
